Table of Contents
Let’s Learn the Concept of Revenue.
In this article, Let’s learn the concept of total Revenue and its underlying concept to understand better the company’s mechanism to analyze its performance.
Total Revenue
The word revenue is a business’s profit from selling its products or services at a specific price.
Revenue is the initial point where a company starts to determine its income statement profits and loss statement. It determines the net income usually generated after covering up all the expenses in running and selling the product or services. The total expenses include the product manufacturing cost, Administrative, & General expenses, Promotional Marketing expenses, Interest expense to debtors, Dividends to stakeholders, and income tax payment to Government for the given year. Total Revenue is the essential underlined item in the business consideration.
Total revenue analysis is one of the many different options company has to determine its yearly performance. It is a helpful insight into business or invertor’s perspective. Two of the most common revenues are total and marginal Revenue to evaluate the business’s current performance.
The objective of Total Revenue (TR)
A good income statement and healthy cash flow are indicators that reflect the company’s stable financial position. Expenses are an inevitable part of the business, yet greater profits or total revenues suggest that the company is well maintaining its production operations, covering all expenses efficiently. The larger the Revenue, the more money company is generating from selling its product or services. It is worthy of your attention in the cover-up all the expenses of the company. The more significant portion of Revenue means you have sufficient income to cover all the operational expenses in the company.
The objective of Total Revenue is to determine the reasons behind the declining total revenues. The reasons could lie in the strategies of the sales and marketing teams while deciding the selling price. From another perspective, you can use the company’s financial health evaluation to resolve the problem areas that need the attention of specialists or make selling price adjustments to the production cost to maximize the company’s profitability.
Total Revenue Calculation Formula
The revenue calculation frequently enumerates the monthly revenues from different account sources in the company grand account records. Let say, for instance, the number of pizzas sold in an hour or the number of medium-sized salad boxes sold throughout the business day. The total daily Revenue would be the quantity (Q) of salad boxes – assume 200, multiplied by its respective Price – say $3 daily. The formula for Total Revenue would be:
∴Total Revenue(TR)=Total Quantity (Q)×Unit Price(P)
Total Revenue (TR)=200×$3
Total Revenue (TR)=$600
The value we can determine from the above calculation is that total Revenue is $600 by multiplying its 200 salad boxes with its selling price of $3.
Total Revenue is essential in profit maximization objective as the company strives to increase its profit by cutting total costs from the generated Revenue. Understanding the cost and revenue relationship plays a pivotal role in increasing production and sales while keeping production costs minimum. As soon as the company intends to increase its production, the cost of the products or service increases.
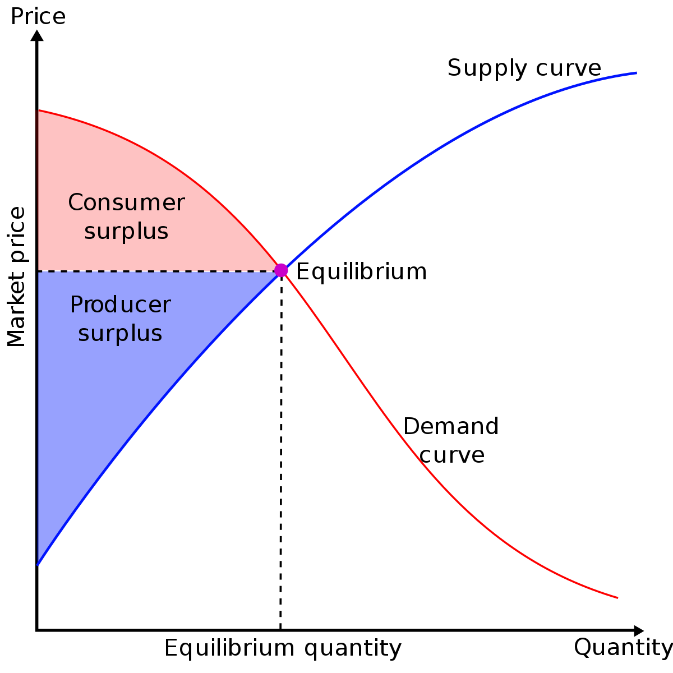
You can get a graphical demonstration of the change in total Revenue concerning its Price in the demand curve graph. It indicates that the company can generate optimum profit by either increasing the number of units or changing its Price concerning market conditions.
What should a company do after calculating Total Revenue?
Being a financial analyst, you can compare Revenue and expenses once you have calculated the company’s total Revenue. It helps to analyze whether it is making significant profits in its production operations or whether its costs are in deficit compared to its revenues.
If the company is facing a downturn in financial performance, you need to adjust the financial budget and the company’s expenses. Changing product selling prices is one way to increase Revenue. In the case of rising prices, some consumers might choose competitive products with lower prices. The financial decisions for price adjustments should positively impact the company eventually.
Total Revenue helps make yearly comparisons from its past performance to determine the growth in Revenue throughout those years. You can easily derive it by taking from current to its last available data of revenues. In this way, you can determine if your business has increased its Revenue over the years. The company can make pricing strategies to boost its sales and generate increased total Revenue.
Marginal Revenue (MR)
Marginal Revenue (MR) is the Net Revenue that a company obtains by selling additional units of a product.
MR is vital to measure the effects of increasing the additional products or service units into the production. How much it helps to boost the company profit is underlined objective. However, marginal Revenue, when it reaches its maximum point, follows the law of diminishing return. It results in reduced output profit while increasing the production unit, affecting the marginal production cost with reduced Revenue. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost both become equal at this point, indicating no profit. It, therefore, starts to deplete the profit in covering up the production cost.
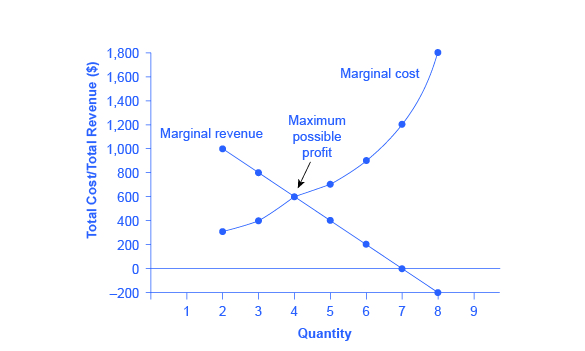
MR Calculation Formula
Let’s define it as the change in Total Revenue that results from a decrease or increase of one unit of output. In other words, it is the additional Revenue generated from the total Revenue by changing the output unit in selling goods. Let’s assume the additional net output of goods to the total Revenue by selling a (n) number of product units rather than (n-1).
ΔTR/ΔQ=Marginal Revenue(〖MR〗_n)
〖〖TR〗_n-〖TR〗_(n-1)=MR〗_n
Where as
〖TR〗_n=Total Revenue of (n)units
〖TR〗_(n-1)=Total Revenue from (n-1)units
〖MR〗_n=Marginal revenue fron nth Unit
n=additional number of units
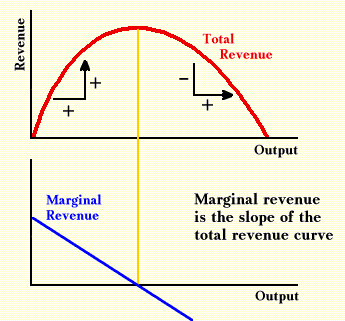
Marginal Revenue (MR): The Slope of Total Revenue
To determine MR, divide the change in total Revenue by change in sold units. MR creates the slope of the total revenue curve. Total Revenue is helpful to calculate the marginal Revenue.
Let’s assume the dairy product company that produces ice cream. It sells its one ice cream for a selling price of $5 per each ice-cream for its first 100-unit production. The total Revenue for its ice cream should be $500 (100 units*$5) if the company intends to change its Price to sell its following 100 units for a selling price of $6 a unit. Then its total Revenue would be $600 ($6*100).
The company wants to determine the MR for each additional unit produced during the increased selling price starting at 101st. The total Revenue is a decisive factor in its calculation. First, find the change in Total Revenue, which is $100 ($600-$500). The next step is to determine the difference in the selling price of $1 ($6-$5). Thus, MR by producing 101st unit from the changed selling price contributes to $100 profit.
(($600-$500))/(($6-$5))=Marginal Revenue (〖MR〗_n)
〖$600-$500=Marginal Revenue (MR〗_n)
〖∴$100=Marginal Revenue (MR〗_n)
Total Revenue, to precisely determine the company’s well-being in maintaining its score operations based on the product’s demand and Price of the product. In contrast, MR helps the company determine different price and production units’ combinations considering the company’s production capacity. As soon as the company’s marginal cost of production gets more significant than its marginal Revenue, the company stops producing additional units.
Points to Remember: Total Revenue vs. MR
- Revenue is the total amount a company brings into the business profit after selling its products or services.
- The income statement initiates the revenue determination that further equates to net income after all selling and administrative expense deductions.
- TR is the full sale amount from products and services. You can quickly determine it by multiplying the total number of goods or services sold with its unit price.
- MR is the additional revenue generation by selling the additional number of products or services in the company business.
- The company continues its additional good or services generation until it reaches its optimum point where marginal Revenue generates no extra profit, therefore equal to marginal cost.
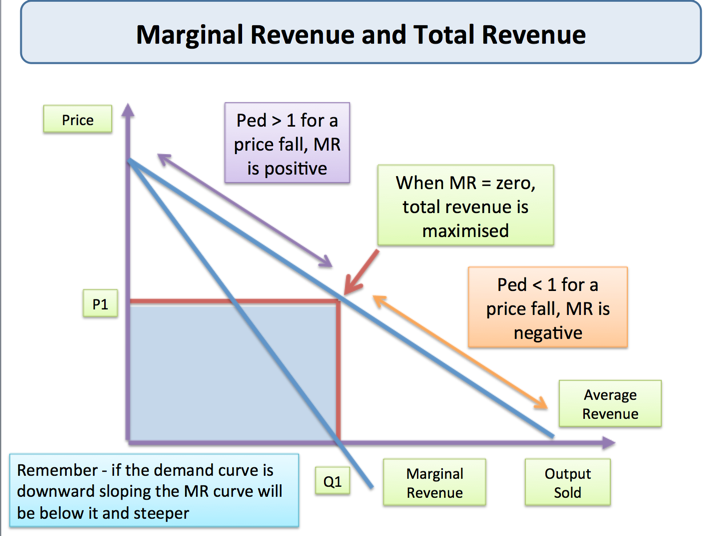
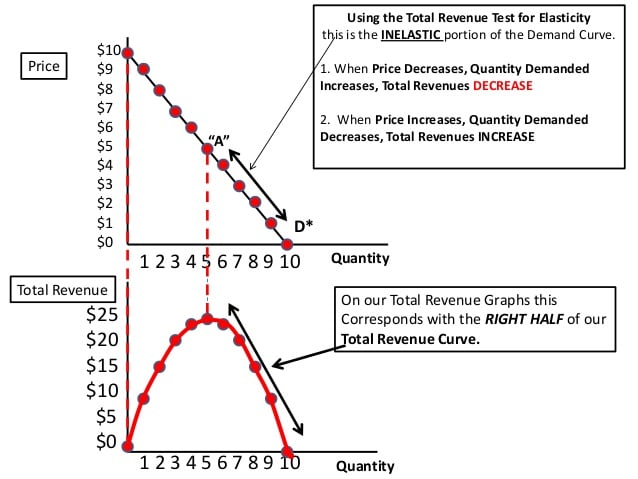
Revenue test for Elasticity
Businesses need the revenue test to determine how much a price change can affect their total income. So, before deciding to change the selling prices of their products, they should assess their effects on total revenues that come from product sales.
This test helps to gauge the type of demand your existing products or services suggest. It allows them to set the Optimum Price to maximize the company’s TR. It assists businesses in understanding the Elasticity of demand and determining whether or not to raise the selling price as part of the revenue generation process. The Elasticity of demand measures the change in TR against price change. It takes into consideration the price change while keeping all other factors constant while determining its Elasticity.
Advantages of Revenue Test
- It helps the company to determine its pricing strategy considering all market conditions.
- The company can further determine how much cushion they have for increasing or decreasing the selling price considering consumer demand relative to its competitors.
- When prices increase does not affect its demand while increasing the revenues, demand is inelastic for that product. It states that price change has an insignificant impact on changing consumer behavior and preferences for the product. In such conditions, the company can quickly increase its Price to generate more revenues.
- On the contrary, if price increase changes to decrease the total revenues, it is considered Elastic demand for such products. Even a slight Price change will result in a significant drop in TR. Therefore, the company should carefully handle the pricing strategy.

